Eco-Smart! Sustainable Exterior Trend 2025: A New Era of Green Design
Eco-Smart! Sustainable Exterior Trend 2025 – The sustainable exterior trend in 2025 is not simply about using “green” materials; it’s about a holistic approach encompassing the entire lifecycle of building materials, from sourcing and manufacturing to installation, maintenance, and eventual disposal or reuse. It’s a commitment to minimizing the carbon footprint and maximizing resource efficiency.

Dominant Eco-Friendly Exterior Materials 2025
The architecture and construction industries are experiencing a surge in innovation, leading to a wider array of eco-friendly exterior materials 2025 than ever before. These materials prioritize sustainability, durability, and aesthetics, allowing designers and homeowners to create beautiful, environmentally responsible spaces.
Reclaimed Wood: A Timeless Classic with a Modern Twist
Reclaimed wood remains a cornerstone of sustainable design, offering a rustic charm and a compelling story of reuse. Sourced from old barns, factories, and other structures, reclaimed wood diverts material from landfills and reduces the demand for newly harvested timber.
- Benefits: Reduced deforestation, unique aesthetic appeal, enhanced structural integrity due to mature wood fibers, historical significance.
- Applications: Siding, decking, trim, accent walls.
- Considerations: Sourcing from reputable suppliers, ensuring proper treatment and stabilization, potential for variations in color and texture.
Bamboo: The Rapidly Renewable Resource
Bamboo is a fast-growing grass that regenerates quickly and requires minimal resources to cultivate. Its strength and versatility make it an excellent alternative to traditional hardwood for exterior applications.
- Benefits: Rapid renewability, high strength-to-weight ratio, natural resistance to pests and decay, aesthetically pleasing texture.
- Applications: Siding, fencing, decking, cladding.
- Considerations: Proper treatment to enhance durability and prevent moisture absorption, sourcing from sustainably managed bamboo farms.
Recycled Plastic: Transforming Waste into Wonder
Recycled plastic is emerging as a significant player in the eco-friendly exterior materials 2025 landscape. Plastic waste, once a major environmental concern, is now being repurposed into durable and weather-resistant building materials.
- Benefits: Diverts plastic waste from landfills, reduces the need for virgin plastic production, resistant to moisture and insects, low maintenance.
- Applications: Decking, siding, fencing, exterior trim.
- Considerations: Ensuring the plastic is properly cleaned and processed, potential for color fading over time, exploring different types of recycled plastic for specific application best suited.
Bio-Based Composites: Nature’s Ingenuity
Bio-based composites combine natural fibers, such as hemp, flax, or rice husks, with bio-resins derived from plant oils or starches. These materials offer a sustainable alternative to traditional composites, with a lower carbon footprint and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
- Benefits: Renewable resources, reduced carbon footprint, lightweight, durable, potential for customization.
- Applications: Siding, cladding, decking, rainscreen systems.
- Considerations: Ensuring the bio-resins are sustainably sourced, evaluating the long-term performance and resistance to weathering, initial cost.
Green Concrete: A Sustainable Foundation
Traditional concrete production is a major source of carbon emissions. Green concrete seeks to mitigate this impact by incorporating recycled aggregates, supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) like fly ash or slag, and other innovative techniques.
- Benefits: Reduced carbon emissions, utilization of waste materials, improved durability and strength in some cases.
- Applications: Foundations, walkways, patios, retaining walls.
- Considerations: Ensuring the SCMs meet performance standards, carefully controlling the mix design, local availability of green concrete options.
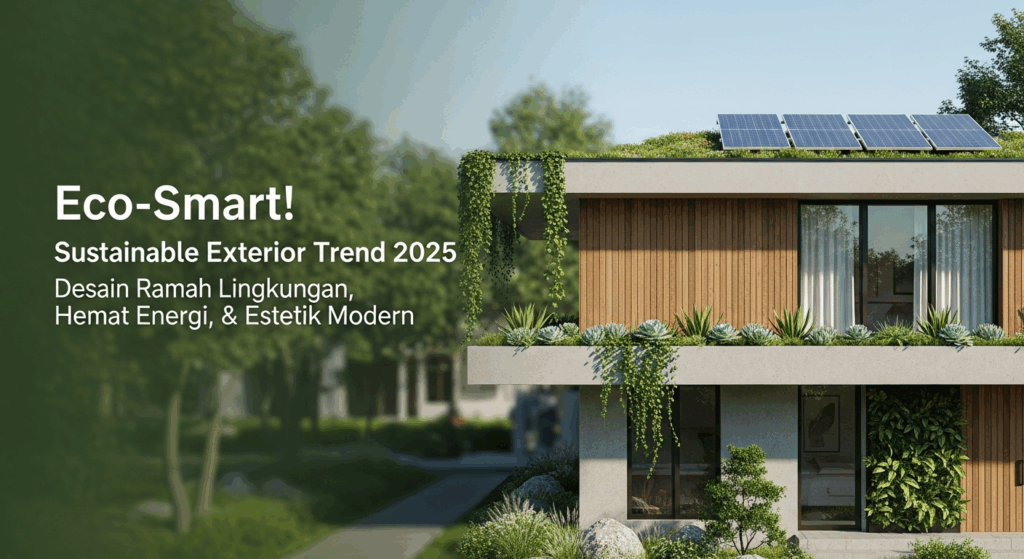
The Rise of Smart Technologies in Sustainable Exteriors
Beyond the materials themselves, smart technologies are playing an increasingly crucial role in enhancing the sustainability of building exteriors.
Smart Glass: Energy Efficiency Redefined
Smart glass, also known as electrochromic glass, can adjust its transparency in response to changing sunlight conditions. This reduces the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning, leading to significant energy savings.
- Benefits: Reduced energy consumption, improved indoor comfort, glare control, aesthetically pleasing design.
- Applications: Windows, skylights, curtain walls.
- Considerations: Initial cost, energy consumption of the electrochromic system, long-term performance and durability.
Solar Panels: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Solar panels are becoming increasingly integrated into building exteriors, providing a clean and renewable source of energy. Advances in technology are making solar panels more efficient, affordable, and aesthetically appealing.
- Benefits: Renewable energy generation, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, government incentives and rebates, increased property value.
- Applications: Roofing, siding, windows, integrated shading systems.
- Considerations: Initial cost of installation, local climate conditions, aesthetic integration with the building design, maintenance requirements.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Water Conservation for Landscaping
Smart irrigation systems use sensors and weather data to optimize water usage for landscaping, preventing overwatering and conserving precious resources.
- Benefits: Water conservation, reduced water bills, healthier plants, automated operation.
- Applications: Gardens, lawns, green roofs, vertical gardens.
- Considerations: Initial cost of installation, sensor maintenance, integration with existing irrigation systems.

The Aesthetic of Sustainability: Bridging Function and Form
The shift towards eco-friendly building materials doesn’t mean compromising on aesthetics. In fact, sustainable design often embraces natural textures, earthy tones, and innovative forms, creating visually stunning and environmentally responsible exteriors.
Biophilic Design: Connecting with Nature
Biophilic design incorporates natural elements and patterns into the built environment, promoting a sense of connection with nature. This approach enhances well-being, reduces stress, and creates more inviting and sustainable spaces.
- Strategies: Incorporating natural light, using natural materials, adding plants and water features, replicating natural patterns.
- Benefits: Improved indoor air quality, reduced stress, enhanced productivity, aesthetic appeal.
- Considerations: Integrating biophilic elements into the building design, maintaining plant life and water features, cost considerations.
Vertical Gardens and Green Walls: Living Art on Exterior Surfaces
Vertical gardens and green walls transform exterior surfaces into living ecosystems, providing insulation, improving air quality, and enhancing visual appeal.
- Benefits: Improved air quality, insulation, reduced urban heat island effect, aesthetic appeal, habitat creation.
- Applications: Building facades, balconies, retaining walls.
- Considerations: Structural support for the green wall, irrigation system, plant selection, maintenance requirements.
Light and Shadow: Natural Elements for Visual Harmony
Sustainable designs often leverage natural light and shadow to create dynamic and visually captivating exteriors. The use of overhangs, louvers, and strategically placed plantings can control sunlight, reduce glare, and enhance the building’s aesthetic appeal.
Color Palettes: Earthy Tones and Natural Hues
Eco-friendly exterior materials 2025 often feature natural color palettes that blend seamlessly with the surrounding environment. Earthy tones, such as browns, greens, and grays, create a sense of harmony and connection with nature.
Regulatory Landscape and Incentives Shaping Eco-Smart Exteriors
Government regulations and incentives are playing a significant role in driving the adoption of eco-friendly exterior materials 2025. Building codes, green building certifications, and financial incentives are creating a more favorable environment for sustainable construction.
Green Building Certifications: Setting the Standard for Sustainability
Certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and Passive House provide a framework for evaluating the environmental performance of buildings and promoting sustainable design practices.
- Benefits: Improved building performance, reduced environmental impact, increased property value, recognition for sustainable design.
- Considerations: Cost of certification, documentation requirements, integration with the building design process.
Government Incentives and Rebates: Making Sustainability More Affordable
Many governments offer incentives and rebates for using sustainable building materials and implementing energy-efficient technologies. These programs can significantly reduce the upfront cost of eco-smart exteriors, making them more accessible to homeowners and developers.
Building Codes and Regulations: Setting Minimum Standards for Sustainability
Increasingly, building codes and regulations are incorporating sustainability requirements, such as minimum energy efficiency standards for building envelopes and restrictions on the use of certain materials.
The Future of Eco-Smart Exteriors: Innovation and Collaboration
The future of eco-smart exteriors is bright, driven by ongoing innovation, collaboration, and a growing awareness of the importance of sustainability.
Emerging Technologies: Pushing the Boundaries of Sustainable Design
Research and development efforts are constantly yielding new and improved eco-friendly exterior materials 2025. Some emerging technologies include self-healing concrete, carbon-sequestering materials, and advanced insulation systems.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Driving Systemic Change
Collaboration between architects, engineers, material scientists, and policymakers is essential for driving systemic change in the construction industry. By working together, these stakeholders can overcome challenges and accelerate the adoption of sustainable building practices.
Circular Economy Principles: Minimizing Waste and Maximizing Resource Use
Circular economy principles are gaining traction in the construction industry, with a focus on minimizing waste, reusing materials, and designing for disassembly. This approach promotes a more sustainable and resource-efficient built environment.
Addressing Challenges and Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Despite the growing interest in eco-smart exteriors, there are still challenges and barriers to adoption that need to be addressed.
Cost Considerations: Balancing Affordability and Sustainability
The initial cost of some eco-friendly exterior materials 2025 may be higher than that of conventional alternatives. However, it’s important to consider the long-term cost savings associated with reduced energy consumption, lower maintenance, and increased durability. Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) can help make informed decisions.
Availability and Accessibility: Ensuring Widespread Access to Sustainable Materials
In some regions, access to a diverse range of sustainable materials may be limited. This can be due to factors such as transportation costs, lack of local suppliers, and limited demand. Governments and industry organizations can play a role in addressing these challenges by promoting the development of local supply chains and supporting small businesses.
Perceived Performance Risks: Addressing Concerns About Durability and Longevity
Some people may have concerns about the durability and longevity of eco-friendly exterior materials 2025. It’s important to provide clear and accurate information about the performance characteristics of these materials, as well as case studies and testimonials from successful projects.
Integration Complexity: Navigating the Design and Construction Process
Integrating eco-friendly exterior materials 2025 into the design and construction process can sometimes be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise. Architects, engineers, and contractors need to be trained in the proper handling and installation techniques for these materials. Early collaboration among stakeholders is key to a successful project.
Showcasing Success Stories: Inspiring Real-World Examples
To illustrate the potential of eco-smart exteriors, let’s look at some real-world examples of buildings that have successfully integrated sustainable materials and technologies.
The Bullitt Center, Seattle: A Living Building Challenge Project
The Bullitt Center in Seattle is one of the most sustainable buildings in the world, designed to meet the rigorous standards of the Living Building Challenge. The building features a rooftop solar array, rainwater harvesting system, composting toilets, and a high-performance building envelope made from locally sourced materials.
The Crystal, London: A Showcase of Sustainable Urban Development
The Crystal in London is a sustainable urban development that showcases Siemens’ technologies for sustainable cities. The building features a double-glazed facade with integrated solar shading, a rainwater harvesting system, and a geothermal heating and cooling system.
The Biomimicry Guild Headquarters, Montana: Learning from Nature’s Design
The Biomimicry Guild Headquarters in Montana is a sustainable building inspired by nature’s designs. The building features a green roof, natural ventilation, and a passive solar design. Its materials are selected with careful consideration for their environmental impact.
Case Study: Sustainable Siding in the Pacific Northwest
A residential project in Oregon successfully utilized reclaimed wood siding, sourced from a deconstructed barn. The siding not only provided a unique aesthetic but also significantly reduced the project’s carbon footprint. The homeowners also utilized a rainwater harvesting system, showcasing a commitment to comprehensive sustainability
Case Study: Recycled Plastic Decking in Florida
A coastal property in Florida opted for recycled plastic decking to withstand the harsh marine environment. The decking is resistant to moisture, insects, and rot, providing a long-lasting and low-maintenance solution. It diverted plastic waste from landfills and helped protect the homeowner’s investment for years to come.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach to Sustainability
Creating truly eco-smart exteriors, requires a systemic approach that considers the entire life cycle of building materials, from sourcing to disposal. A holistic approach leads to the best results and overall reduction of environmental impact.
Embodied Carbon Analysis: Understanding the Environmental Impact of Materials
Embodied carbon refers to the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the extraction, manufacturing, transportation, and installation of building materials. Conducting an embodied carbon analysis can help identify materials with the lowest environmental impact.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Evaluating the Environmental Performance of Buildings
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a comprehensive method for evaluating the environmental impacts of a product or building throughout its entire life cycle. LCA can help architects and engineers make informed decisions about materials selection, energy efficiency, and waste management.
Design for Disassembly (DfD): Planning for the End of Life
Design for Disassembly (DfD) is a design approach that considers the end-of-life of building materials and components. DfD aims to facilitate the reuse, recycling, or repurposing of materials at the end of a building’s lifespan, reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Conclusion
As we approach 2025, the sustainable exterior trend, fueled by innovative eco-friendly exterior materials 2025, is gaining powerful momentum. From reclaimed wood and bamboo to recycled plastic and bio-based composites, the options for creating beautiful and environmentally responsible building exteriors are expanding rapidly. By embracing smart technologies, adopting a holistic approach to sustainability, and addressing the challenges and barriers to adoption, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient built environment. The future of construction is undeniably green, and the exterior of our buildings will be at the forefront of this transformative shift.
